Developers often allocate a significant portion of their time—up to 20%—to managing container configurations, failover protocols, security measures, and other infrastructure-related tasks. These activities divert focus from actual coding. 1
Automation through container orchestration tools can alleviate these burdens. However, there are tens of solutions in the market. See our vetted list of solutions based on B2B user reviews and key functionality:
| Tool | Tool Type | # of employees | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| ActiveBatch | IT automation & orchestration | 533 | 4.4 based on 251 reviews |
| RunMyJobs by Redwood | IT automation & orchestration | 533 | 4.8 based on 140 reviews |
| Stonebranch | IT automation & orchestration | 152 | 4.8 based on 79 reviews |
| Fortra's JAMS | IT automation & orchestration | 9,941 | 4.7 based on 150 |
| Apache Mesos | Multi-cloud container orchestration | 2,277 | 2.8 based on 18 reviews |
| Kubernetes | Multi-cloud container platform | 116 | 4.5 based on 237 reviews |
| Nomad by Hashicorp | Multi-cloud container orchestration | 2,393 | 4.1 based on 10 reviews |
| Amazon Elastic Container Service | Single-cloud container platform | 130,371 | 4.4 based on 311 reviews |
| Azure Container Instances | Single-cloud container platform | 244,900 | 4.3 based on 57 reviews |
| Azure Service Fabric | Single-cloud container platform | 244,900 | 4.4 based on 23 reviews |
| DigitalOcean | Single-cloud container platform | 1,746 | 4.5 based on 593 reviews |
| Google Cloud Run | Single-cloud container platform | 300,114 | 4.5 based on 140 reviews |
| Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) | Single-cloud container orchestration | 300,114 | 4.5 based on 209 reviews |
Ranking is first by sponsorship. Then, top container orchestration tools are sorted alphabetically within their categories. The tools are selected based on:
- The number of employees: 100+ employees on LinkedIn.
- B2B reviews: 10+ user reviews on B2B review platforms.
1.) ActiveBatch
ActiveBatch is an enterprise workload automation and job scheduling software that can orchestrate various tasks across various platforms including Windows and non-Windows environments, including containerized workloads, data integration, cloud automation, and IT processes.
Its features include change management, reporting and monitoring, security & governance, SLA management, Scale on-demand with Managed Queues. ActiveBatch users can benefit from unique features like:
- Super REST API adapters to access any server, application, or service using pre-built or low-code
- Job step library with production-ready functions for efficient process orchestration.
- Flow Control Job Steps to drag and drop jobs within workflows.
Explore more on ActiveBatch via the video:
More on ActiveBatch regarding its features, latest developments and pros & cons.
2.) RunMyJobs
RunMyJobs by Redwood is job scheduling and automation platform delivered as SaaS. It offers a central point of control for automating tasks, orchestrating processes, and managing jobs.
RunMyJobs supports multiple platforms and integrates with various enterprise systems, allowing users to automate a wide range of tasks, including those involving containerized applications. It provides features like:
- Support for 25+ scripting languages to improve flexibility and collaboration
- Customizable escalations and alerts to configure process SLAs and thresholds
- Lightweight and auto-updating agents to minimize resource use and manual intervention
- Built-in disaster recovery to integrate solutions for recovering data and maintaining operations
- AI-powered documentation assistant to answer questions, summarize content, and provide sources via a searchable avatar on the help site.
Learn how to integrate your entire technology stack for end-to-end processes with RunMyJobs:
Explore features, strenghts and weaknesses of RunMyJobs.
3.) Stonebranch
Stonebranch UAC centralizes container orchestration, microservices scheduling, and workload automation, enabling seamless integration of IT processes across hybrid environments. Stonebranch UAC offers:
- End-to-End Docker orchestration to automate containerized and legacy workloads.
- Lifecycle management to Simplify promotion of tested processes with “bundle & promote.”
- Centralized credential management to secure registry and application connections.
- Microservices scheduling that is compatible with HTTP, REST, SOAP, JMS, and WebSphereMQ.
- Proactive monitoring of Web-based dashboards ensure real-time visibility.
4.) Fortra’s JAMS
Fortra’s JAMS is an enterprise job scheduling and workload automation solution designed to streamline and manage complex workflows across diverse IT environments. While not a dedicated container orchestration tool, JAMS offers features that complement containerized application management:
- Cross-platform job scheduling to orchestrate and automate tasks across various platforms, including on-premises systems and cloud environments, ensuring seamless integration with containerized applications.
- Event-driven automation to utilize event-based triggers to initiate workflows in response to specific conditions, such as the completion of a container deployment or changes in application status.
- Monitoring and reporting to gain real-time visibility into job statuses and system performance through centralized dashboards, facilitating proactive management of containerized workloads.
5.) Kubernetes
Kubernetes, or K8s, is an open-source container orchestration platform that can automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It allows developers to define complex workloads and their scaling policies.
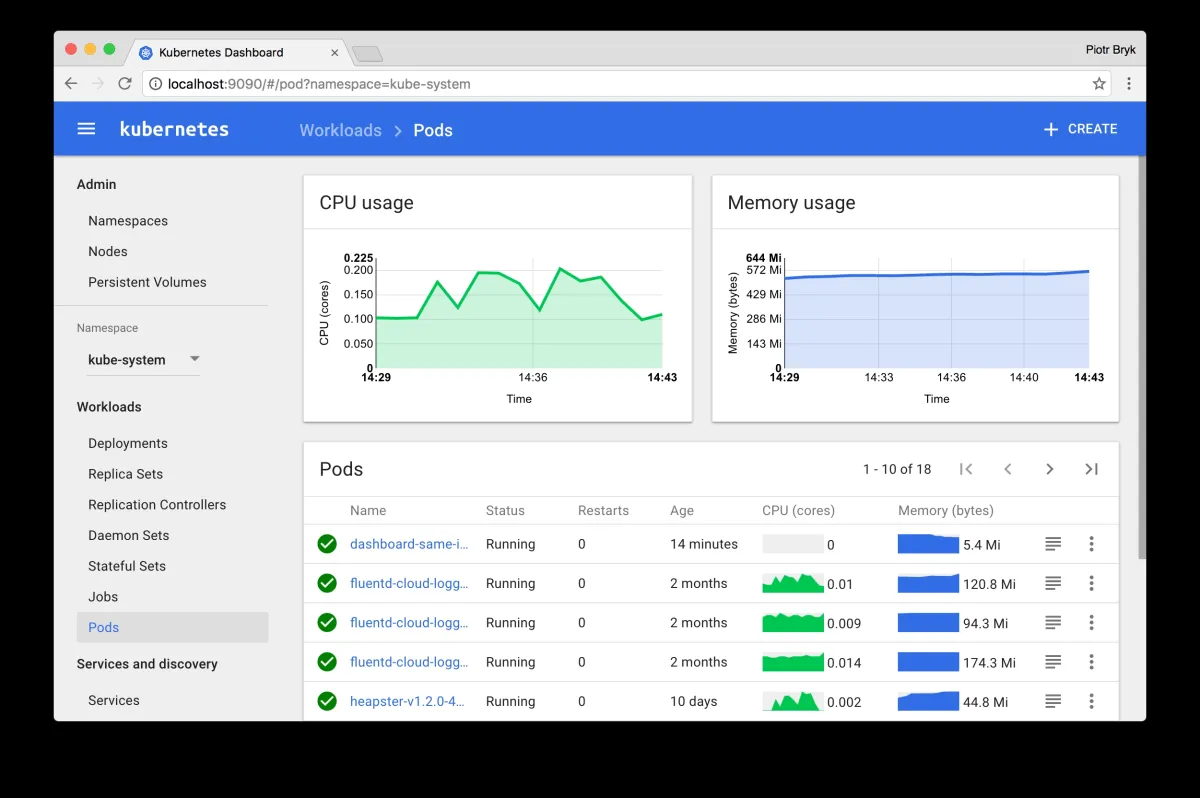
Kubernetes can manage workloads on a cluster of servers, abstracting infrastructure details from developers. It supports various extensions and integrations, enabling users to create custom solutions that suit their specific needs.
The visual below depicts Kubernetes’ operations:
6.) Apache Mesos
Apache Mesos is an open-source cluster manager designed for resource sharing and distributed system management. It acts as a kernel for data centers, abstracting resources and enabling fine-grained resource management.
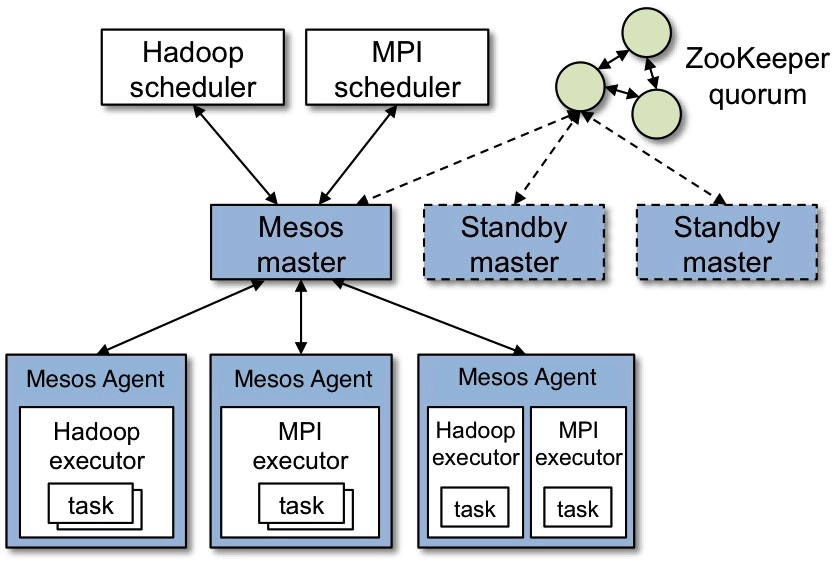
Mesos can run diverse workloads, including containers, big data applications, and other distributed systems. Its architecture allows the development of frameworks like Apache Marathon and Apache Aurora, which are used for orchestrating applications on top of Mesos.
The image illustrates the architecture of Apache Mesos:
7.) Hashicorp Nomad
Hashicorp Nomad is an orchestration tool designed for deploying and managing containerized applications, non-containerized applications, and batch processing jobs. It supports multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployments, providing a unified workflow for deploying applications across different environments.
Nomad offers a simplified approach to orchestration, focusing on ease of use and operational simplicity. It includes features like autoscaling, job scheduling, and integration with other Hashicorp tools, such as Consul for service discovery and Vault for secret management.
8.) Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
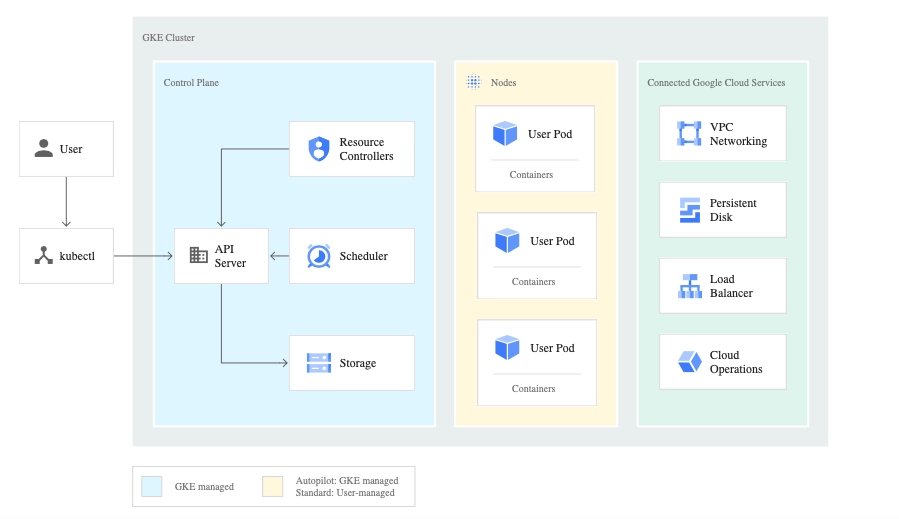
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a managed Kubernetes service offered by Google Cloud Platform. It provides a simplified and scalable platform for deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications. GKE automates many operational tasks, including cluster management, scaling, and monitoring.
It integrates with other Google Cloud services, offering security and compliance features. GKE provides support for both standard Kubernetes workloads and advanced use cases, such as serverless computing with Knative. It is a popular choice for organizations looking for a fully managed Kubernetes solution with strong integration with Google Cloud’s ecosystem.
9.) Google Cloud Run
Google Cloud Run is a managed platform for deploying and running containerized applications in a serverless environment. It abstracts infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus on building applications without worrying about server provisioning or scaling.
Cloud Run automatically scales applications based on demand and supports both stateless HTTP services and background processing. It is built on the open-source Knative project, ensuring compatibility with standard containerized workloads.
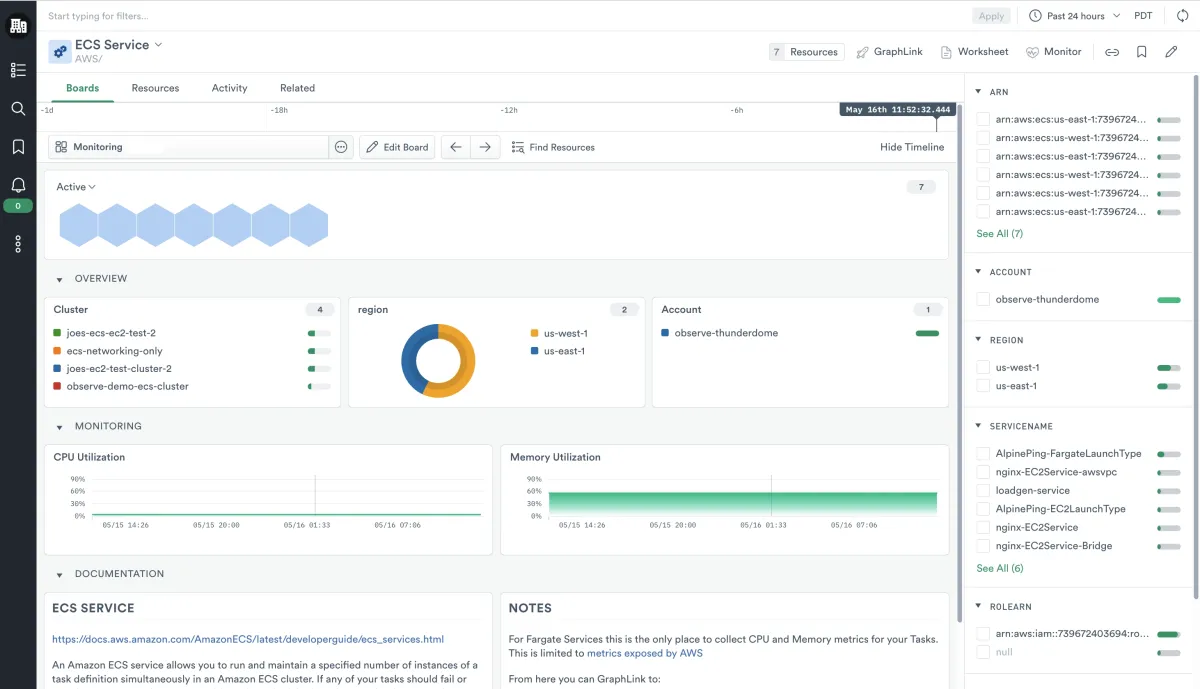
10.) Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS)
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a managed container orchestration service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It allows users to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications using AWS infrastructure.
ECS supports various orchestration patterns, including Fargate, a serverless mode for running containers without managing servers, and EC2, which provides full control over the underlying infrastructure. ECS integrates with other AWS services, offering security, monitoring, and scaling features. It is a popular choice for organizations seeking a managed container service within the AWS cloud ecosystem.
11.) OpenShift Container Platform
Red Hat OpenShift is an enterprise-grade Kubernetes-based platform for deploying and managing containerized applications. It provides additional features on top of standard Kubernetes, such as a developer-friendly interface, integrated CI/CD pipelines, and enhanced security. OpenShift supports multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployments, offering flexibility for enterprises with diverse infrastructure requirements.
Key features of Azure Service Fabric include operators, which automate complex tasks, and an integrated service catalog for rapid deployment of pre-built applications.
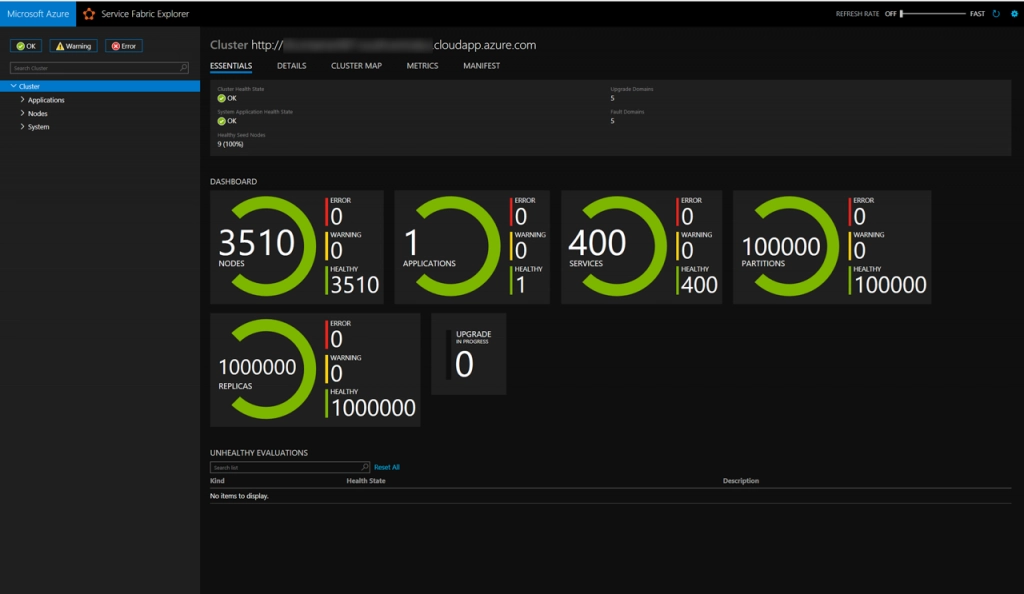
12.) Azure Service Fabric
Azure Service Fabric is a distributed systems platform developed by Microsoft to build and manage scalable, reliable applications in the cloud. It supports a wide range of workloads, including microservices, containers, and stateful applications.
Service Fabric provides tools for orchestration, health monitoring, and auto-scaling, making it easier to manage complex applications. It is highly integrated with other Azure services, offering security, compliance, and monitoring features. Service Fabric can run in various environments, including Azure, on-premises, or different clouds, providing flexibility for enterprises with diverse infrastructure needs.
13.) DigitalOcean
DigitalOcean is a cloud infrastructure provider offering various services, including container orchestration through its managed Kubernetes platform. DigitalOcean Kubernetes allows users to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications with ease. It provides a simplified interface for creating and managing Kubernetes clusters, focusing on developer-friendliness and operational simplicity.
DigitalOcean’s Kubernetes service is designed for smaller-scale deployments and startups but can also scale to meet enterprise needs. It offers integrations with other DigitalOcean services and supports various third-party tools.

FAQs
What is a container orchestration tool?
A container orchestrator is a system designed for managing containers and their related workloads. It allows developers to define container images, a configuration file and automates container deployment across multiple operating systems.
By acting as a cluster management tool, it provides functionalities like load balancing to ensure smooth traffic distribution.
How does container orchestration work?
Container orchestration works by automating the deployment, scaling, and operation of containers in a cluster. It uses a container definition file to define the characteristics of each container, such as its image, environment variables, and resource requirements. Once the containers are defined, they are automatically deployed to the appropriate nodes within the cluster.
The orchestration tool continuously monitors the health of the running containers. If a container fails, the tool automatically restarts it or re-allocates it to another node. This automatic recovery ensures high availability and resiliency.
Additionally, the orchestration tool provides a centralized interface for container management, allowing users to control, scale, and update their containers as needed, ensuring efficient and smooth operation of containerized applications.
Why Use Container Orchestrators?
A container orchestration tool ensures that containers deployed within a cluster are managed efficiently. It dynamically handles resource allocation, ensuring that each container receives the appropriate CPU, memory, and storage resources based on its requirements. This process is automated, reducing the need for manual intervention and enabling scaling as demand fluctuates.
When containers are deployed, the orchestration tool manages them to maintain high availability and reliability. It monitors container health and automatically restarts or reassigns containers in the event of a failure, ensuring continuous service. This automation and resilience are key reasons to use container orchestration tools, as they facilitate scalable, reliable, and efficient container management.
How to choose a container orchestration tool?
These are 8 steps to consider while choosing the best container orchestration tool for your organization:
1.) Compatibility with existing infrastructure: Ensure the tool integrates with your current infrastructure, including operating systems, hardware, cloud providers, and DevOps tools.
2.) Scalability and flexibility: Consider the scalability requirements of your applications. Choose a tool that can handle your current workload and scale with future growth. Flexibility in supporting multi-cloud and hybrid environments is also crucial.
3.) Ease of use and deployment: Evaluate the user interface, documentation, and community support. A tool with a straightforward setup and clear documentation can reduce learning curves and deployment time.
4.) Integration with other tools: Determine whether the tool integrates with other services and applications in your ecosystem, such as CI/CD pipelines, monitoring, and logging solutions.
5.) Security and compliance: Assess the security features of the orchestration tool, including role-based access control (RBAC), encryption, and compliance with industry standards. Ensure it meets your organization’s security policies.
6.) Cost: Review the pricing structure, including licensing fees, infrastructure costs, and additional costs for add-ons or support. Choose a tool that aligns with your budget while providing the necessary features.
7.) Support and community: Consider the level of support available, including vendor support, community forums, and third-party resources. A strong community can be valuable for troubleshooting and guidance.
8.) Operational requirements: Evaluate the operational needs, such as high availability, disaster recovery, and monitoring capabilities. Ensure the tool supports these features to meet your operational goals.
Further reading
Explore more on orchestration tools by checking out:
- Compare 12 Data Orchestration Tools Based on 800+ Reviews
- Compare 18 Orchestration Tools: 5,000+ Reviews & Features
- Top 10 Process Orchestration Tools based on 5,200 Reviews
External sources
- 1. Getting the most from cloud services and containers | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company
- 2. What is Kubernetes? A Guide to Container Orchestration - Stackify. Stackify
- 3. Apache Mesos - Architecture.
- 4. GKE cluster architecture | Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) | Google Cloud.
- 5. Amazon Elastic Container Service - Observability Cloud documentation.
- 6. Microsoft Brings Container Orchestration to Azure Service Fabric, for Windows and (Soon) Linux - The New Stack. The New Stack

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.