During my 2 decades of experience helping enterprises adopt automation & AI, accounting and other financial processes were a focus area for me due to their rules-based nature. Based on these experiences, I identified the top 6 accounting processes that have been automated with RPA along with real-life examples:
- Reporting
- Journal Entry Automation
- Account Reconciliation
- Financial Close
- Account Payable (AP)
- Account Receivable (AR)
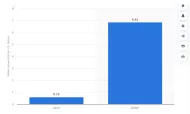
~%70 of the accountants surveyed rely on spreadsheets, increasing both time spent on financial statements as well as the risk of inaccurate results.1 The data also highlight that it takes an average of 7 days to complete the closing process that shifts data from temporary accounts to permanent ones.
Explore the most important automatable processes in accounting:
Which accounting processes can be automated?
Since most of the business processes in accounting are repetitive, time-consuming, and require high precision, RPA bots can reduce costs and increase accuracy.
Robotic process automation bots can handle the following processes in accounting:
1. Reporting
RPA can be used to automate the generation of different kinds of financial reports, such as:
- Periodic financial statements, such as balance sheets and income statements,
- Compliance reports
- Profit and loss (P&L) reports
- Expense reports
- And tax reports
- Customer data setup
Real-life example:
For instance, Ikano Bank leveraged RPA to automate updating customer records, like name changes, significantly improving data accuracy. A bot was built to replace 10 employees, who would have taken hundreds of days to manually update records, completing the backlog in weeks instead, saving the company weeks of work.
This allowed for quicker and more accurate generation of financial reports, such as balance sheets and P&L statements.2
- Improved data accuracy, leading to more reliable financial reports.
- Faster generation of financial reports, reducing time spent on manual tasks.
To learn more, read our article on RPA reporting.
2. Journal Entry Automation
- Journal entry creation: The processes of recording business transactions, including dates, debits and credits, transaction descriptions, and reference numbers.
- Journal posting: Journal entries are then posted to the record-keeping system called general ledger (GL) to sort, store, and summarize the transactions. The general ledger forms the basis of a company’s financial statement and income statement.
Automating this process offers benefits like:
- Using OCR to extract accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR) data in various formats from Excel sheets or other ERP systems.
- Enriching input data from AP and AR processes.
- For example, in cases of invoices with no purchase orders, companies need to trace back the orders’ origins. But if such entries are automated, the digital footprint would make it easy to know where each order’s invoice is.
- Supplementing the journal entries with comments, supporting documents, and reconciliations in real time.
- Loading the journal’s data automatically onto ERP systems.
The main benefit of automating journal entries is the time it saves for the accounting department. Once the close period arrives, the journal entries, which have already been entered throughout the month, are ready for posting to the general ledger. This automation eliminates the need for manual data entry, ensuring faster and more accurate updates.
Real-life example:
At Danske Bank, RPA has been used to automate customer service processes and sanction checks. By automating customer data management, the bank ensures that journal entries are more accurate and consistently updated across financial systems, which speeds up the journal posting process. Robots are handling the equivalent of 300 full-time employees’ work, representing 1.3 percent of the entire workforce.3
- Increased accuracy of journal entries by ensuring data consistency across systems.
- Reduced manual intervention in the journal posting process, speeding up financial operations.
3. Account Reconciliation
Account reconciliation is the process of comparing the company’s financial records against external records to find information about the money spent and received, and balance the final figures. These procedures may have different steps in different businesses. There are:
- Bank Reconciliation to check the validity of issued checks, and ensure that all transactions have been recorded.
- Vendor Reconciliation to compare customer invoices to vendor accounts. When companies make numerous transactions with clients, the buyer and seller can have different records about the balance due to issues in bank payments, manual errors, etc. This process allows both parties to identify and reconcile differences and have the same view about the outstanding balance.
- Intercompany (IC) Reconciliation is similar to vendor reconciliation but takes place when different legal entities of the same company (e.g. its subsidiaries) are trading with one another. It is to identify any unrecorded transactions or balances in the books, mistakes in invoicing, loans, deposits, and interests.
This is a process that relies heavily on balance sheets, PDF invoices, and accounting records. RPA bots can ease the process because they can easily acquire data, match payment details to company data, and provide real-time visibility into reconciliation performance which is ideal for handling repetitive tasks.
Real-life example:
First Abu Dhabi Bank (FAB) automated bank reconciliations, significantly improving the speed and accuracy of matching transactions. By using RPA, the bank reduced errors and ensured that the reconciliation process was completed in a fraction of the time, making the entire process more efficient.
The process, which previously took up to seven days, was reduced to one day, resulting in an 88% increase in efficiency and a 75% improvement in turn-around times, saving 840 hours annually.4
- Minimized errors, ensuring more accurate reconciliation.
- Reduced reconciliation time by automating the transaction matching process.
4. Financial Close
Financial close is a process to verify and adjust account balances at the end of specific periods to produce financial reports. These reports inform stakeholders of the company’s financial performance over the period. Challenges that face accountants in financial close which are automatable are:
- Data preparation challenges include:
- Manual data entry
- Data manipulation tasks due to different business departments sharing data in different formats
- Errors, missing receipts, invoices, or journal entry documents
- No access to real-time data about finance flow
RPA bots help businesses complete the financial close cycle quickly and accurately, by:
- Importing spreadsheets from multiple resources or accounting software to have access to all accounting data, and automating data entry into financial systems to reduce errors
- Running automated checklists related to closing accounting books to automatically identify and highlight issues.
- Tracking progress, timelines, and approvals in the financial close process to identify potential issues and bottlenecks.
- Comparing financial data using reconciliation depositories or reconciliation management tools.
Real-life example:
Banca Progetto used robotic process automation to automate high-volume tasks like account renewals, significantly reducing the manual workload. By speeding up these processes, they were able to close their books more efficiently and meet strict reporting deadlines, showcasing how RPA enhances the financial close process.5
- Renewed 400 to 500 accounts daily within a month, drastically improving throughput.
- Reduced manual work during the financial close process.
- Accelerated the financial close, meeting reporting deadlines more effectively.
5. Account Payable (AP)
Account payable is a highly automatable process because it relies on repetitive tasks such as data extraction, invoice validation, and payment processing. Implementing RPA in AP will allow cycle time reduction, cost reduction, and preventing manual errors.
Real-life example:
At Acciona, RPA was implemented to automate key processes, including HR, procurement, and back-office operations. One of the significant successes was automating the task of registering and de-registering temporary contracts. This process, which previously required 15 minutes per contract, now takes only a fraction of the time with the help of RPA software robots.6
- Automated the registration and de-registration of nearly 20,000 contracts in 2019, drastically reducing processing time.
Feel free to read more about RPA use in accounts payable, steps, benefits, and technologies used, in our article AP automation
6. Account Receivable (AR)
Account receivable is the opposite of account payable. It is the process of recording, accounting, and collecting payments that are owed to the company. Account receivable is similar to AP in the matter of automation.
AR tasks include:
- Extracting data from supplier invoices and customer orders
- Matching invoices to orders, and orders to offers
- Routing invoices for approvals
- Filing and retrieving invoices
- Processing payments
Implementing RPA in accounts receivable helps companies optimize customer invoicing and payments, as well as deliver reports and analytics on the status of AR processes.
Real-life example:
At Ikano Bank, RPA was used to streamline payment deferrals and customer profile management, which directly impacts accounts receivable. By automating these processes, the bank ensured that invoices were processed quicker, payments were tracked more efficiently, and customer satisfaction improved.7
- Improved the speed of invoice processing and payment tracking.
- Increased customer satisfaction through faster service.
Read in detail about account receivable automation in our article order management for businesses.
How should companies implement RPA accounting to their processes?
There are 4 main approaches to automating accounting that we see in enterprises:
- End-to-end solutions: ERP software provides accounting functionality and ERP providers try to offer automation through the improvement of their solution and automation
- Best-of-breed solutions that provide out-of-the-box automation: The similarities between different companies’ accounting processes are more than the differences. New vendors are relying on machine learning to automate accounting end-to-end
- Customizable automation solutions: RPA software is one of the most flexible automation tools. They can help automate company-specific processes however companies need to be aware that they need to keep some RPA experts in-house for cost-effective bot maintenance.
- An end-to-end solution that is integrated with automation solutions: Enterprises are risk averse in their core processes and thoroughly test new solutions before deploying them. However, they can try best-of-breed solutions or customizable automation solutions to make their existing system smarter.
If you feel like your business could benefit from account payable software, we provide data-driven, sortable lists of vendors.
Impact of implementing RPA in accounting
According to a research article about automating accounting processes, implementing RPA in accounting will help companies:
- Avoid financial fraud
- Improve accounting information quality
- Promote auditing efficiency
An example of these is Lenovo Group, whose internal audit department previously assigned three employees to spend five days each month manually downloading and reviewing thousands of expense reports and invoices.
With the introduction of RPA, a robot now completes this task in just five hours, saving 1,500 labor hours annually. This automation has greatly reduced manual work and increased efficiency in their auditing processes.8
Also, a client of Accelirate, a leading North American firm in the pulp, paper, and personal care sectors, faced difficulties managing the high volume of invoices from vendors, warehouses, and managers. Manual processing led to frequent errors, inefficiencies, and delays, jeopardizing data accuracy and payment timeliness.
By partnering with Accelirate, the client adopted an RPA-based Invoice Processing solution. This new financial reporting system seamlessly integrated with their existing setup, optimizing operations, minimizing errors, and achieving quick returns on investment.9
RPA implementation will also allow companies to
- Run leaner accounting organizations,
- Help accountants focus on strategic initiatives that can help grow the business.
Why is robotic process automation important for accounting?
Accounting is manual and mostly rule-based, making it a great candidate for automation. Accountants can either adopt domain specific accounting automation solutions or adopt RPA to build automation for their work. Automation will free accountants from mundane tasks, instead, accountants can focus on strategic decision-making and business processes.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is transforming finance departments by automating repetitive tasks such as invoice processing, financial reporting, and payroll management. RPA in accounting drives cost savings by reducing labor costs and eliminating manual tasks, allowing finance teams to focus on high-value activities like financial forecasting and cash flow management.
By automating time-consuming processes, robotic process automation solutions enhance workflow efficiencies and operational performance. This digital transformation empowers finance teams to achieve greater accuracy and speed, optimizing both financial planning and overall efficiency.
For more on RPA
For more on RPA in finance, read our article Top RPA Use Cases / Applications in Finance
To learn more about RPA, you can read:
If you are interested in applying robotic process automation in other businesses, feel free to read our article Top 100+ RPA Use cases / Applications/ Examples
If you are ready to try using RPA accounting in your business, you can use our prioritized, comprehensive list of RPA vendors to choose the right RPA vendor for your business.
External Links
- 1. Process Automation in Accounting and Finance | IMA.
- 2. Ikano Bank Puts People at the Center with Automation | UiPath.
- 3. Danske Bank Expands Citizen Developer Program and Intelligent Automation | UiPath.
- 4. First Abu Dhabi Bank's Journey into Intelligent Automation | UiPath .
- 5. Banca Progetto Accelerates its Operations with RPA | UiPath.
- 6. Acciona - RPA Use Cases in Infrastructure & Energy | UiPath.
- 7. Ikano Bank Puts People at the Center with Automation | UiPath.
- 8. Lenovo Group Integrates Intelligent Technologies with RPA | UiPath.
- 9. Accelirate's Automated Invoice Processing Brings Significant ROI for Manufacturing Company - Accelirate.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.